RestAssured
API Flow

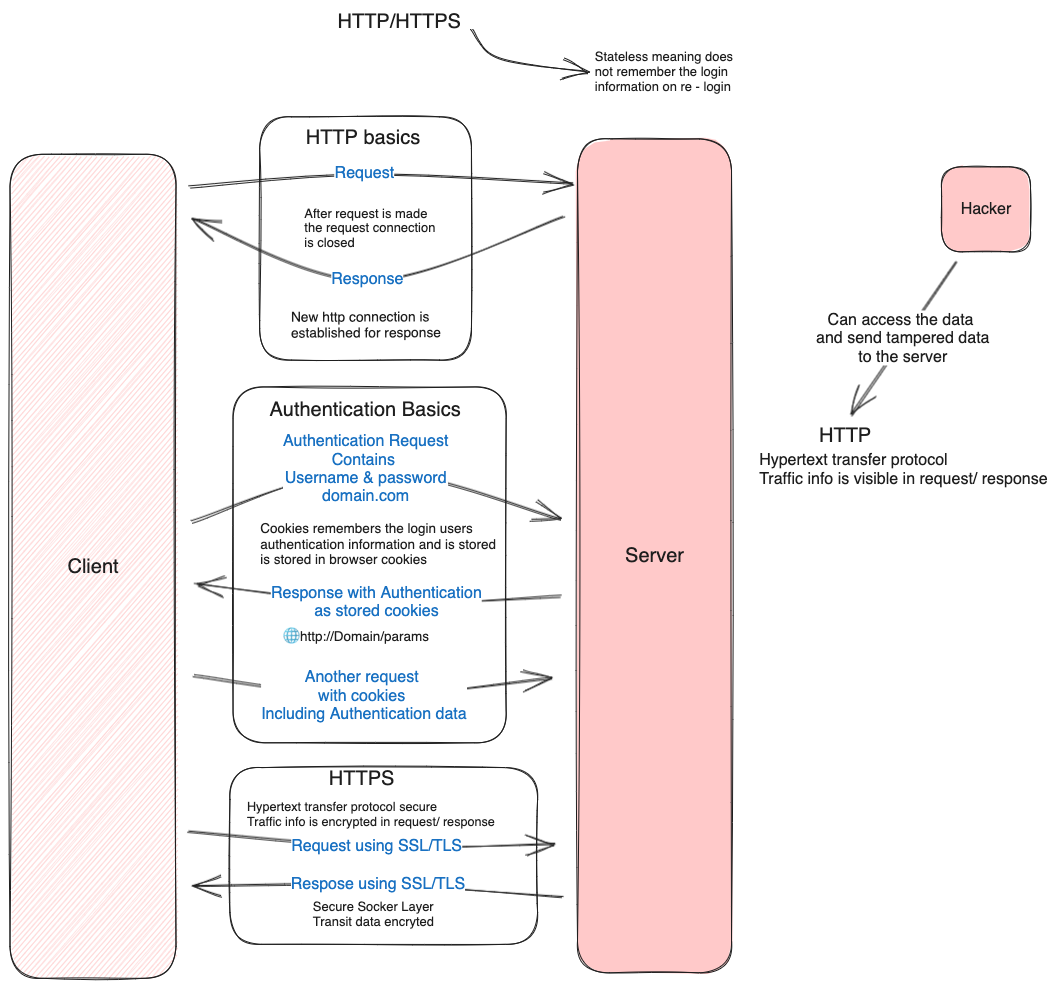
Http Basics
HTTP methods
GET Asks to get the resource at the requested URL. POST Asks the server to accept the body info attached. It is like GET request with extra info sent with the request. HEAD Asks for only the header part of whatever a GET would return. Just like GET but with no body. TRACE Asks for the loopback of the request message, for testing or troubleshooting. PUT Says to put the enclosed info (the body) at the requested URL. DELETE Says to delete the resource at the requested URL. OPTIONS Asks for a list of the HTTP methods to which the thing at the request URL can respond PATCH: For partial updates.
- 1xx (100 – 199): The response is informational
- 2xx (200 – 299): Assures successful response
- 3xx (300 – 399): You are required to take further action to fulfill the request
- 4xx (400 – 499): There’s a bad syntax and the request cannot be completed
- 5xx (500 – 599): The server entirely fails to complete the request
Example
https://domain.com/?key1=value1&key2=value2
HTTP Request
Request Line
- The HTTP method used
- The request URI
- The HTTP protocol version
Zero or more headers
- User-Agent: lets the server identify the application, operating system, vendor, and version.
- Connection: controls the network connection. In other words, kill or continues the connection after the transaction.
- Cache-Control: specifies browser caching policies.
- Accept-Language: indicates what all languages(natural) the client can understand.
- Accept-Charset
- Accept-Encoding
- Authorization
- Content-Length
- Content-Type
- Cookie
- Expect
- From
- Host
- If-Match
- If-Modified-Since
- In-None-Match
- If-Range
- If-Unmodified-Since
- Max-Forwards
- Proxy-Authorization
- Range
- Referer
- TE
An optional request body
- _Request body may either be in the form of XML or JSON
HTTPS Response
- A status.
- Collection of Headers.
- A Body.
RestAssured without Static imports
import org.testng.Assert;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import io.restassured.RestAssured;
import io.restassured.response.Response;
import io.restassured.response.ValidatableResponse;
import io.restassured.specification.RequestSpecification;
public class WithoutBDDStyle {
static RequestSpecification requestSpecification;
static Response response;
static ValidatableResponse validatableResponse;
@Test
public void oldMethodOfRestAssured() {
RestAssured.baseURI = "http://dummy.restapiexample.com/api/v1/employees";
// Create a request specification
requestSpecification = RestAssured.given();
// Calling GET method
response = requestSpecification.get();
// Let's print response body.
System.out.println(response.prettyPrint());
// Validate Response
validatableResponse = response.then();
// Get status code
validatableResponse.statusCode(200);
// Check status line is as expected
validatableResponse.statusLine("HTTP/1.1 200 OK");
}
@Test
public void oldMethodOfRestAssuredUsingTestNG() {
RestAssured.baseURI = "http://dummy.restapiexample.com/api/v1/employees";
// Create a request specification
requestSpecification = RestAssured.given();
// Calling GET method
response = requestSpecification.get();
// Let's print response body.
System.out.println(response.prettyPrint());
// Get status line
Assert.assertEquals(response.getStatusLine(), "HTTP/1.1 200 OK");
// Get status code
Assert.assertEquals(response.getStatusCode(), 200);
}
}
RestAssured withStatic imports BDD style
Example
- Resource URL: https://bookstore.toolsqa.com/
- Parameter: BookStore/v1/Books
Characteristics of REST
- Uniform interface
- Client Server separation
- Stateless
- Layered System
- Cacheable
- Code-on-demand(Eg - Flash Video Player)
Rest API Connectors
- _Client
- _Server
- _Cache
- _Resolver
- _Tunnel
Components in Rest
- _Origin Server
- _User Agent
- _Gateway
- _Proxy
Rest Data Elements
- Resource
- Resource Identifier(URI)
- Resource Metadata
- Representation (Entire Request or Response)
- Representation Metadata(Headers- content-type, content-length, User-Agent, Connection, Accept-Encodin)
Query Parameter And Path Parameter JsonPath XmlPath
Create Json Object with Json Simple
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.googlecode.json-simple/json-simple -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.googlecode.json-simple</groupId>
<artifactId>json-simple</artifactId>
<version>1.1.1</version>
</dependency>
JSONObject requestParams = new JSONObject();
requestParams.put("userId", "TQ123");
requestParams.put("isbn", "9781449325862");
JSONObject.toJSONString()
request.header("Content-Type", "application/json");
request.body(requestParams.toJSONString());
Serialization
Serialization is a process where you convert an Instance of a Class (Object of a class) into a Byte Stream. This Byte Stream can then be stored as a file on the disk or can also be sent to another computer via the network. Deserialisation in Opposite of Serialization.

ObjectOutputStream o = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("//File Name"));
Animal animal = new Animal("Cow");
o.writeObject(animal);
o.close();
Deserialization
FileInputStream fileStream = new FileInputStream(new File(fileName));
ObjectInputStream objectStream = new ObjectInputStream(fileStream);
Object deserializeObject = objectStream.readObject();
objectStream.close();
fileStream.close();
Authentication
- Being able to authenticate with Credentials
Basic Authentication(Auth)
- Does using Authentication headers. ie username and Password is sent in the URL.
given().auth().basic("your username", "your password").get("your end point URL");
Challenge Response Mechanism This means that it waits for the server to challenge rather than send the credentials directly.
given().auth().preemptive().basic("your username", "your password").get("your end point URL");
Digest Authentication
It uses a digestive key in subsequent requests. If at all it is intercepted by an eavesdropper, he will get access only to the transaction performed and not the user password.
given().auth().digest("your username", "your password").get("your end point URL")
Form Authentication
given() .auth().form("your username", "your password").post("your end point URL")
given().auth().form("your username", "your password", new FormAuthConfig("/perform_signIn","user","password"))
OAuth Authentication
//Oauth 1
given().auth().oauth(consumerKey, consumerSecret, accessToken, tokenSecret).get("your end point URL")
// Oauth 2
given().auth().oauth2("Access token").get("your end point URL")
Authorisation
- Being able to provide valid access. ie (Admin and Employee users )
Put Request
OST request
- 201 with a location header pointing to the new resource.
- 400 if the new item is not created.
PUT request
- 204 for OK/SUCCESS (but no content).
- 200 for OK with Content Body (Updated response).
- 400 if the data sent was invalid. https://toolsqa.com/rest-assured/put-request-using-rest-assured/
To Be continued
https://toolsqa.com/rest-assured/delete-request-using-rest-assured/ https://qaautomation.expert/2023/10/12/rest-assured-tutorials/
Jira Practice Api's
Cookie-based authentication Api
Session Filter explanation
Attachment and Multipart upload
Extract Response as using extract().asString()
HTTPs relaxed https certifications
OAath 2.0
Access token clinet ID , google sign in Grant type(autherisation code and client credentials)
- Hitting the Access Code URL and getting the access code
- Hitting the Access Token URL and getting the Access Token
- Hitting the actual request with the access token
![[Pasted image 20231123100710.png]]
TOken in Response ![[Pasted image 20231123101213.png]]
![[Pasted image 20231123101952.png]]
![[Pasted image 20231123102141.png]] ![[Pasted image 20231123124455.png]] ![[Pasted image 20231123102325.png]] ![[Pasted image 20231123102358.png]]
![[Pasted image 20231123103612.png]] Access Code
![[Pasted image 20231123123202.png]]
Access Token
![[Pasted image 20231123123433.png]]
Actual Request ![[Pasted image 20231123123315.png]]
Client Credential
![[Pasted image 20231123124427.png]]
![[Pasted image 20231123124636.png]]
https://qaautomation.expert/2023/10/12/rest-assured-tutorials/
Serialisation and Deserialisation using POJO
![[Pasted image 20231123152504.png]] ![[Pasted image 20231123162831.png]]
Request Response Spec Builder
![[Pasted image 20231123180330.png]]
![[Pasted image 20231123180618.png]]
JWT token RestAssured
Form data
![[Pasted image 20231123222103.png]] ![[Pasted image 20231123222155.png]]
Using Rest Assured ![[Pasted image 20231123223410.png]]
![[Pasted image 20231123223744.png]]
Loggig ![[Pasted image 20231124153450.png]]
Rest Assured Framework
Dependency
Rest Assured dependency includes JsonPath and XmlPath
Rest Assured's dependency declaration comes before (JUnit or TestNG) dependency to make sure that the correct version of Hamcrest is used
- JsonPath: Used for parsing and extracting data from JSON responses.
- XmlPath: Used for parsing and manipulating XML responses.
- Hamcreast is used for assertions.
- json-schema-validator is used for validating Json Schema Jacson Gson
Static Imports
import io.restassured.RestAssured.*;
import io.restassured.matcher.RestAssuredMatchers.*;
import org.hamcrest.Matchers.*;
import io.restassured.module.jsv.JsonSchemaValidator.*;